Why Does the Doctor Advise So Many Ultrasounds During Your Pregnancy?
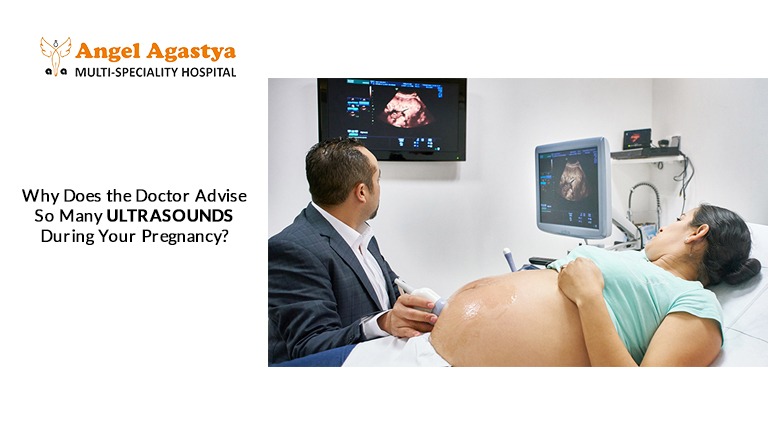
Are you overwhelmed by the number of ultrasounds your doctor is recommending? While some scans are essential, are all of them truly necessary—or just adding to your stress and expenses? Let’s break down the facts and uncover the real reason behind multiple scans during pregnancy!
Introduction
Pregnancy is a beautiful journey filled with excitement, joy, and anticipation. However, it can also bring moments of uncertainty and concern for expectant mothers. To ensure the best possible health for both the mother and the growing baby, prenatal care is essential. One of the most common and crucial aspects of this care is ultrasound examinations. These scans provide a detailed view of the baby’s development, helping doctors monitor key milestones and detect any potential concerns early on.
While some women may feel that frequent ultrasounds are unnecessary or overwhelming, they serve a vital purpose in ensuring a smooth pregnancy. Ultrasounds help track fetal growth, confirm the baby’s position, and assess the placenta’s health. Additionally, they can detect structural abnormalities, measure amniotic fluid levels, and identify complications such as fetal distress or placental insufficiency. Early detection of such issues allows healthcare providers to take timely action, reducing risks and improving pregnancy outcomes.
Though ultrasounds are generally safe, it’s natural for expectant mothers to question their necessity. Understanding their importance can ease concerns and reinforce confidence in prenatal care. These scans are not just medical procedures—they are valuable tools that provide reassurance and help ensure a safe and healthy journey to motherhood.
The Role of Ultrasound in Pregnancy
Ultrasound in pregnancy has become an indispensable tool in modern obstetric care. These non-invasive scans use high-frequency sound waves to create images of the developing fetus. Here’s how ultrasounds contribute to prenatal care at different stages of pregnancy:
Early Pregnancy Ultrasounds
- Confirming Pregnancy: An early ultrasound confirms the presence of a gestational sac and a developing embryo, providing early confirmation of pregnancy.
- Determining Gestational Age: Early ultrasounds are crucial for accurately determining gestational age, which is essential for establishing an expected due date.
- Ruling Out Ectopic Pregnancy: An ectopic pregnancy occurs when the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, typically in the fallopian tube. Ultrasound helps identify an ectopic pregnancy early, which is critical for timely medical intervention.
- Assessing Viability: Early ultrasounds can detect the fetal heartbeat and confirm if the pregnancy is progressing normally.
First Trimester Ultrasound
- Nuchal Translucency (NT) Scan: This specialized ultrasound, typically performed between 11 and 13 weeks of pregnancy, measures fluid accumulation at the back of the baby’s neck. An increased nuchal translucency may be associated with a higher risk of chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome. This information helps guide further testing and counseling.
- Early Screening for Birth Defects: Certain structural abnormalities can sometimes be detected in the first trimester through ultrasound.
- Checking for Multiple Pregnancies: Early ultrasounds help determine if a woman is carrying twins or more, which affects prenatal care and delivery planning.
Second Trimester Ultrasound
- Anatomy Scan: This comprehensive ultrasound, typically performed between 18 and 22 weeks of pregnancy, allows for a detailed assessment of the fetus’s anatomy. It helps identify potential structural abnormalities, such as heart defects, spina bifida, and cleft lip or palate.
- Determining the Baby’s Sex: If desired, the baby’s gender can be determined during this scan. (We do not support SD at all; this is just a piece of information)
- Assessing Placental Position: The location of the placenta is important to determine if conditions like placenta previa (when the placenta covers the cervix) are present.
- Detecting Signs of Preterm Labor: The ultrasound can measure cervical length and help predict the risk of preterm labor.
Third Trimester Ultrasound
- Fetal Growth Monitoring: In the later stages of pregnancy, ultrasounds help monitor the baby’s growth and development, ensuring the baby is growing at an appropriate rate.
- Assessing Amniotic Fluid Levels: Too much or too little amniotic fluid can indicate potential complications that may require medical intervention.
- Placental Function: Ultrasounds can help assess placental function, identifying conditions such as placental insufficiency, which can restrict blood flow to the baby.
- Checking the Baby’s Position: As delivery approaches, an ultrasound helps determine whether the baby is in the correct head-down position for birth.
Identifying Potential Complications
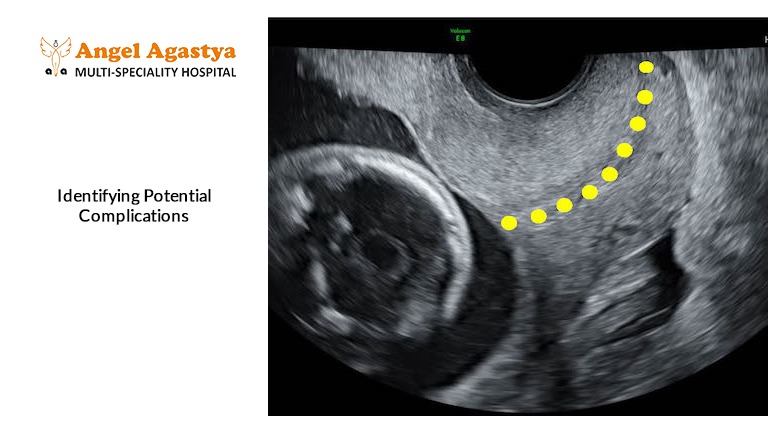
Ultrasound in pregnancy plays a crucial role in identifying potential complications that could affect the health of the mother and baby. Some common concerns that ultrasound helps diagnose include:
- Placental Abnormalities: Ultrasound can help identify placental abnormalities such as placenta previa and placental abruption, both of which can lead to complications if not monitored.
- Fetal Abnormalities: Ultrasounds can help detect a wide range of fetal abnormalities, including congenital heart defects, neural tube defects (such as spina bifida), and other structural anomalies.
- Multiple Gestations: In pregnancies with twins, triplets, or more, ultrasound examinations are essential for monitoring the growth and development of each fetus, assessing the placenta, and identifying potential complications such as twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome.
- Umbilical Cord Issues: Some babies have umbilical cord abnormalities, such as a single artery umbilical cord or cord entanglement, which need close monitoring.
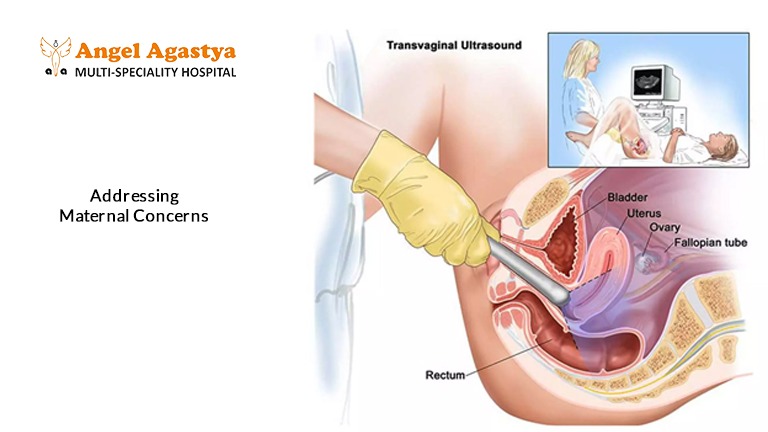
Addressing Maternal Concerns
While some women may feel overwhelmed by the number of ultrasounds during pregnancy, it’s essential to recognize their significance in modern obstetric care. These scans are not just routine procedures; they provide crucial insights into fetal development, helping doctors ensure a safe and healthy pregnancy. By monitoring fetal growth, assessing the baby’s position, and detecting potential abnormalities, ultrasounds play a vital role in guiding medical decisions and offering reassurance to expectant mothers.
Each ultrasound serves a specific purpose. Early scans confirm the pregnancy, detect multiple fetuses, and establish an accurate due date. As the pregnancy progresses, mid-trimester ultrasounds check for structural development, while third-trimester scans assess fetal position, amniotic fluid levels, and placental health. In high-risk pregnancies, more frequent ultrasounds are necessary to monitor conditions like gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, or intrauterine growth restriction.
Though the number of scans may seem excessive to some, they are performed with the baby’s best interests in mind. Modern ultrasound technology is safe and non-invasive, making it an essential tool for prenatal care. Understanding their importance helps expectant mothers feel more confident, informed, and reassured throughout their pregnancy journey, knowing that their baby’s well-being is being closely monitored.
Is Ultrasound in Pregnancy Safe?
- Numerous studies have shown that routine prenatal ultrasounds are safe for both mother and baby.
- The amount of ultrasound energy used during these examinations is minimal and does not pose any known risks to the developing fetus.
- Unlike X-rays, ultrasound does not use ionizing radiation, making it a safe and preferred method of fetal imaging.
How Many Ultrasounds Are Too Many?
- There is no set number of ultrasounds required during pregnancy. Some women may need only two or three, while others with high-risk pregnancies may require more frequent monitoring.
- Doctors typically recommend ultrasounds based on medical necessity rather than as a routine practice.
What If an Ultrasound Detects an Issue?
- If an abnormality is found, the doctor may recommend further testing, such as amniocentesis, chorionic villus sampling (CVS), or Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT).
- Additional ultrasounds may be required to monitor the condition and prepare for necessary medical interventions or special care at birth.
Conclusion
Ultrasound in pregnancy plays a vital role in modern prenatal care, providing valuable information about the health and development of the fetus. While some women may find the frequency of these scans somewhat overwhelming, it’s important to remember that they are an essential tool for identifying and addressing potential complications, ensuring the best possible outcomes for both mother and baby. If you have any concerns about the number of ultrasounds recommended for you, discuss them with your healthcare provider to better understand their necessity and benefits.
By staying informed and embracing ultrasound as a key component of prenatal care, expectant mothers can gain reassurance about their baby’s well-being and enjoy a safer, healthier pregnancy journey.
FAQs
1. Why is Ultrasounds in Pregnancy necessary?
Answer: Ultrasound in Pregnancy is essential for monitoring the baby’s development, detecting abnormalities, and ensuring maternal and fetal health. It provides real-time imaging of the fetus, placenta, and amniotic fluid, helping doctors make informed decisions throughout pregnancy.
2. How many times should Ultrasounds in Pregnancy be done?
Answer: The number of ultrasounds varies based on the pregnancy type. A low-risk pregnancy typically requires at least three ultrasounds—one in each trimester. However, high-risk pregnancies may need more frequent Ultrasound in Pregnancy scans to monitor complications like fetal growth restriction, placental issues, or multiple gestations.
3. Is Ultrasound in Pregnancy safe for the baby?
Answer: Yes, Ultrasound in Pregnancy is considered completely safe. It uses high-frequency sound waves, not radiation, making it a non-invasive and risk-free imaging method for assessing fetal health and development. No known harmful effects have been reported when performed by trained professionals.
4. What can be detected through Ultrasound in Pregnancy?
Answer: Ultrasound in Pregnancy can detect:
- Gestational age and due date estimation
- Fetal growth and development
- Congenital anomalies like heart defects or spina bifida
- Placental position (e.g., placenta previa)
- Amniotic fluid levels
- Multiple pregnancies (twins, triplets, etc.)
5. When is the first Ultrasound in Pregnancy performed?
Answer: The first Ultrasound in Pregnancy is typically performed between 6 to 9 weeks to confirm pregnancy, check the fetal heartbeat, and rule out ectopic pregnancy. It helps determine gestational age and an estimated due date.
6. What happens during the Anatomy Scan Ultrasound in Pregnancy?
Answer: The Anatomy Scan, performed between 18-22 weeks, is a detailed Ultrasound in Pregnancy that examines the baby’s organs, brain, spine, limbs, and heart. It can also reveal the baby’s gender (if desired). This scan is crucial for detecting any structural abnormalities early.
7. Why do some women need additional Ultrasound in Pregnancy scans?
Answer: Additional Ultrasound in Pregnancy scans are needed if:
- There are concerns about fetal growth restrictions
- The placenta is in an abnormal position
- The amniotic fluid levels are too high or low
- The mother has gestational diabetes or high blood pressure
- The baby is not in the correct position for delivery
8. Can Ultrasound in Pregnancy predict labor timing?
Answer: While Ultrasound in Pregnancy cannot accurately predict labor timing, it can estimate fetal size, cervical length, and amniotic fluid levels, which may indicate the likelihood of preterm or overdue delivery. In late pregnancy, an ultrasound helps check if the baby is in the head-down position for birth.
9. Is 3D/4D Ultrasound in Pregnancy necessary?
Answer: 3D/4D Ultrasound in Pregnancy is not medically necessary but is sometimes recommended for detailed imaging of fetal structures, especially if a congenital anomaly is suspected. Many parents opt for 3D/4D scans for bonding purposes, as they provide clear images of the baby’s face and movements.
10. What should I do if an abnormality is detected during Ultrasound in Pregnancy?
Answer: If an Ultrasound in Pregnancy detects an abnormality, your doctor may recommend further tests such as amniocentesis, chorionic villus sampling (CVS), or Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT). Additional ultrasounds may be scheduled to monitor the condition. A fetal medicine specialist can guide you through the next steps based on the findings.
