Introduction:
Bartholin Cyst: Ever felt a lump down there and panicked?
You’re not alone.
Let’s explore Bartholin cysts, a common concern for many women.
Problem Agitation:
Lumps near the vagina can be alarming, triggering worry and confusion. You might wonder if it’s serious and what next?
Solution Introduction:
This guide sheds light on Bartholin cysts, explaining their causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Breathe easy, knowing you’re not alone and empowered to manage your health.
Understanding Bartholin Cysts:
What are Bartholin Cysts?
Bartholin glands are located on either side of the vaginal opening and produce fluid that helps with lubrication during sex. Sometimes, the duct leading out of these glands can become blocked, causing fluid to accumulate and form a cyst.
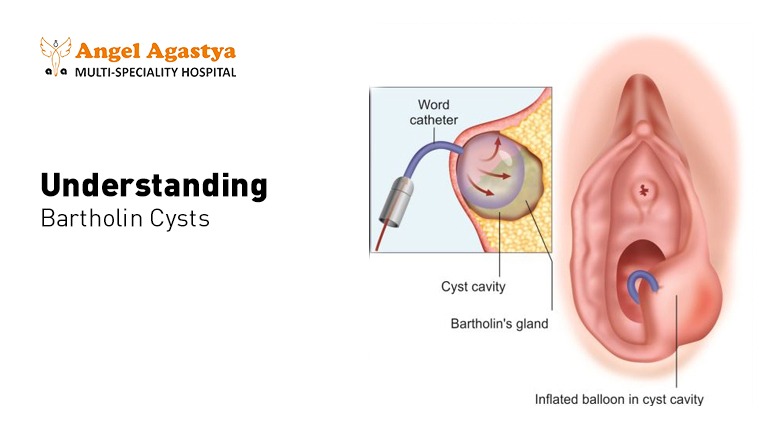
Types of Bartholin Cysts:
There are two main types of Bartholin cysts:
- Simple cyst: This is a painless, fluid-filled lump that might not cause any discomfort.
- Abscess: If bacteria gets trapped inside the blocked duct, the cyst can become infected and inflamed, leading to pain, redness, and swelling. This is called a Bartholin abscess.
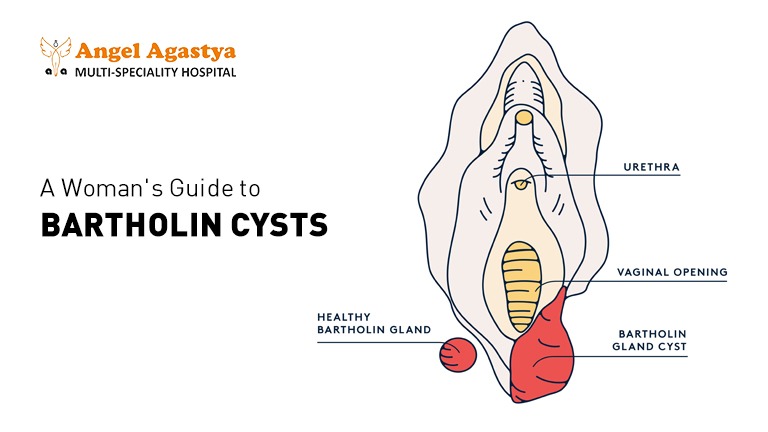
Symptoms and Signs:
Symptoms of a Bartholin cyst can vary depending on the type and size. Here’s what to watch for:
- A lump near the vaginal opening, usually on one side
- Discomfort or pain, especially during sex or sitting
- Redness or swelling in the area (in case of an abscess)
- Difficulty walking or sitting (in severe cases)
Important to Note: Some women might not experience any symptoms at all, especially with a small, simple cyst.
When to Seek Help:
Don’t Ignore It:
While some cysts might not be bothersome, seeking medical attention is important, especially if you experience:
- A large, painful lump
- Redness, swelling, or fever (signs of an infection)
- Difficulty walking or sitting

Diagnosis:
Your doctor can diagnose a Bartholin cyst through a physical examination. In some cases, additional tests like a swab for infection or an ultrasound might be needed.
Addressing Concerns:
The good news is that Bartholin cysts are usually benign and treatable. Early diagnosis and proper management can help prevent complications.
Treatment Options:
The treatment for a Bartholin cyst depends on the size and severity. Here are some common approaches:
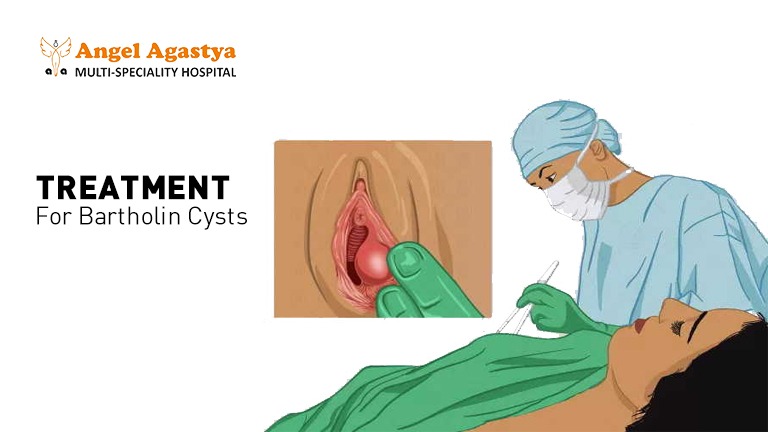
- Watchful waiting: For small, non-bothersome cysts, your doctor might recommend monitoring the situation and see if it resolves on its own.
- Warm Sitz Baths: Soaking in warm sitz baths (shallow baths with warm water) several times a day can help promote drainage and reduce discomfort.
- Antibiotics: If the cyst is infected (abscess), your doctor will prescribe antibiotics to fight the bacterial growth.
- Drainage procedures: In some cases, minimally invasive procedures like aspiration (using a needle to drain the cyst) or marsupialization (creating a new opening for drainage) might be recommended.
Surgery (Rare Cases):
In very rare situations, surgery might be necessary for complex or recurring cysts.
Living with a Bartholin Cyst:
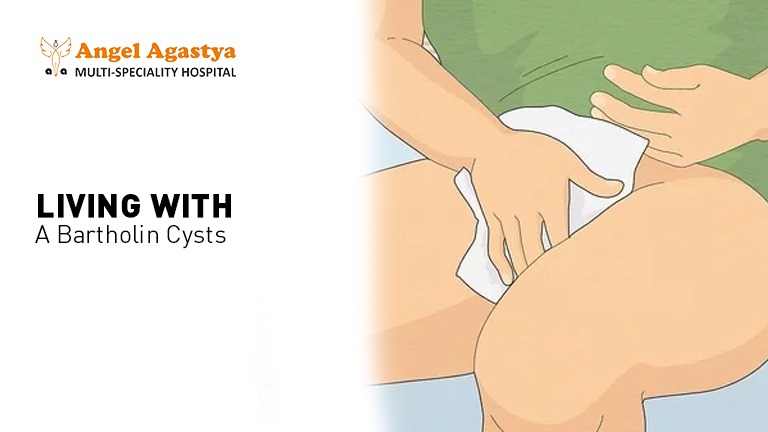
Maintaining Hygiene:
Practicing good hygiene can help minimize the risk of infection. This includes keeping the genital area clean and dry, wiping from front to back after using the toilet, and wearing cotton clothes.
Taking Control:
Knowledge empowers you to manage your health. By understanding Bartholin cysts and the available treatment options, you can make informed decisions about your care in consultation with your doctor.
What Patient Say About Bartholin Cyst Removal..
Summary:
Bartholin cysts are fluid-filled lumps near the vagina, often caused by a blocked gland. They can be uncomfortable but are usually benign and treatable. While some cysts might not cause any symptoms, seeking medical attention is important if you experience pain, fever, or a large lump. This guide empowered you with information about diagnosis, treatment options, and how to manage a Bartholin cyst. Remember, open communication with your doctor is key to ensure the best course of action for your individual needs.
FAQs:
- What causes Bartholin cysts?
Several factors can contribute to it, including:
* Bacterial infection
* Trauma or irritation in the genital area
* Tight-fitting clothing
* Previous Bartholin cyst or abscess
- Are Bartholin cysts sexually transmitted infections (STIs)?
No, they are not sexually transmitted infections (STIs). While bacteria can sometimes become trapped in the blocked duct and cause an infection (abscess), this is not the typical cause of a cyst.
- Can Bartholin cysts affect my fertility?
They typically have minimal impact on fertility. The glands are located near the vaginal opening and don’t directly connect to the reproductive organs. However, a large or infected cyst might cause discomfort during sex, potentially affecting sexual activity.
- How can I prevent Bartholin cysts?
There’s no guaranteed way to prevent cysts, but practicing good hygiene can help minimize the risk of infection, which can contribute to abscess formation. This includes:
* Keeping the genital area clean and dry.
* Wiping from front to back after using the toilet.
* Wearing cotton underwear that allows for breathability.
- What happens if a Bartholin cyst bursts?
If a Bartholin abscess bursts on its own, the pus will drain, which might provide some relief. However, this also increases the risk of further infection. It’s important to see a doctor for proper evaluation and treatment even if the cyst bursts.
- Are there any home remedies for them?
While warm sitz baths can be helpful for promoting drainage and reducing discomfort, it’s crucial to consult a doctor before trying any home remedies. Using harsh soaps, douches, or applying topical ointments without medical advice can irritate the area and potentially worsen the condition.
- Can I still have sex with a Bartholin cyst?
Whether you can have sex with it depends on the severity and discomfort level. A small, painless cyst might not cause any problems during sex. However, a large or infected cyst can be painful and make sex difficult or uncomfortable. It’s best to discuss this with your doctor to determine what’s right for you.
- What are the long-term effects of Bartholin cysts?
With proper treatment, They typically don’t have any long-term effects. However, untreated or recurrent infections can lead to complications like scarring or blocked ducts, making future cysts more likely.
- Will I get another Bartholin cyst after treatment?
While uncommon, Bartholin cysts can recur, especially if the underlying cause isn’t addressed. Recurrence is more likely if the cyst was drained instead of completely removed (marsupialization).
- Are there any support groups for women with Bartholin cysts?
While there might not be specific support groups solely dedicated to it, online forums and communities focused on women’s health can offer support and connection with others who might have experienced similar issues. Additionally, consider joining support groups for vulvar health conditions, as Bartholin glands are located near the vulva.
Remember, the most important resource for support and information is your doctor. Don’t hesitate to ask questions and discuss any concerns you might have.

