Does Age Affect Fertility? – A Guide for Time-Conscious Dreamers About Age and Fertility:
Keep Thinking about Age and Fertility?
Imagine this: You and your partner have built a fulfilling life together, and the whispers of starting a family are growing louder. But a question lingers in the back of your mind regarding Age & Fertility – how will your age impact your chances of getting pregnant?

This blog post delves into the realities of age and fertility, offering both scientific insights and emotional support. Whether you’re actively trying to conceive or simply considering your options, understanding the influence of age empowers you to make informed decisions about your family planning journey.
The Power of Choice: Hope Beyond the Numbers
The good news is, advancements in reproductive medicine offer various options for hopeful parents at different stages of life. While age is a factor, it doesn’t have to be a barrier. This blog equips you with knowledge and practical advice to navigate your fertility journey with confidence. With the right information and support, you can create a family on your own timeline.
Understanding the Biology: A Look Inside the Body’s Clock
Let’s break down the biological aspects of age-related fertility decline. Here, we’ll explore two key areas:
- Female Age and Fertility by Decade: A woman’s fertility naturally declines with age. This is primarily due to a decrease in the quantity and quality of eggs. As women age, the number of healthy eggs available for ovulation diminishes. Additionally, the remaining eggs might have chromosomal abnormalities, reducing the chances of a successful pregnancy.
Age and Fertility, biggest two stress for women!
Here’s a breakdown of how fertility typically changes for women across different age groups:

- 20s: This is generally considered the peak time for female fertility with a high number of healthy eggs.
- 30s: Fertility remains good, but it gradually starts to decline.
- 40s: The decline in fertility accelerates as the number and quality of eggs decrease significantly.
- Late 40s and Early 50s: Conception becomes naturally more challenging due to a low number of healthy eggs remaining.
- Male Age and Fertility: While male fertility doesn’t have a strict deadline like women’s, sperm quality can decline with age. This can manifest as a decrease in sperm count, motility (movement), and morphology (shape).
Science with a Human Touch: Exploring Reliable Studies On Age and Fertility
The information presented here is based on reliable sources and scientific studies. Here are some key takeaways:
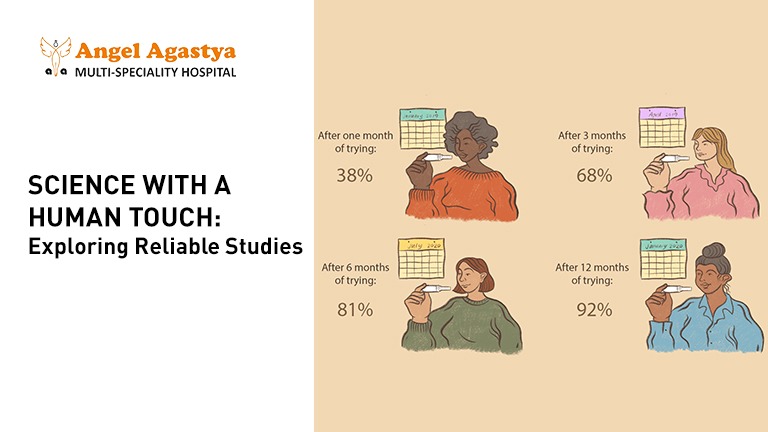
- A study published in the journal Human Reproduction Update found that a woman’s chance of conceiving naturally within a month is around 20% in her 20s, but it declines to 5% by her 40s.
- Research from the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM) suggests that while male fertility remains somewhat stable compared to women’s, sperm quality can decrease after age 40, potentially impacting the chances of natural conception.
Taking Charge On Age & Fertility: Optimizing Your Fertility at Any Age
Now that we understand the science behind age and fertility, let’s explore what you can do! Here are some proactive steps to consider:

- Optimizing Your Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial for overall well-being and can also support fertility health. This includes:
- Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Exercising regularly, but avoiding excessive strain.
- Maintaining a healthy weight.
- Getting enough quality sleep.
- Managing stress through techniques like meditation or yoga.
- Maximizing Your Chances: There are additional strategies specific to men and women:
- For Women Age and Fertility: Consider prenatal vitamins even before conception to support egg health. Some studies suggest that CoQ10 supplements might also be beneficial, but consult your doctor before starting any supplements.
- For Men: Age and Fertility Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and wearing loose-fitting underwear can all contribute to sperm health.
- Considering Alternative Paths for Age and Fertility: If you’re facing age-related fertility challenges, various fertility treatments can be explored with your doctor. These might include:
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): This is a process where an egg is fertilized by sperm outside the body and then implanted in the uterus.
- Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): A specialized technique used in IVF where a single sperm is injected directly into an egg.
- Donor eggs or sperm: This option might be considered for couples facing significant fertility challenges.
Facing the Emotional Journey of Age & Fertility
Age-related fertility concerns can evoke a range of emotions, from anxiety and disappointment to frustration and even grief. It’s important to acknowledge these feelings and seek support.

Building Your Support System:
- Talking to your partner openly and honestly about your concerns can strengthen your bond and provide emotional support during this journey.
- Consider connecting with support groups or online communities specifically for couples facing fertility challenges. Sharing experiences and emotions with others who understand can be incredibly helpful.
- A therapist can also be a valuable resource for managing emotions and navigating the complex decisions you might face.
Myths and Facts:
1. Myth: Infertility is solely a women’s issue.
Fact: Infertility affects both men and women equally
2. Myth: Age doesn’t affect male fertility.
Fact: Male fertility declines with age, although not as drastically as female fertility
3. Myth: If you’re healthy, you can’t have fertility problems.
Fact: Being healthy doesn’t guarantee fertility; factors like genetics and reproductive health play significant roles.
4. Myth: Infertility is always a result of a serious medical condition
Fact: Infertility can be caused by various factors, including hormonal imbalances, structural issues, and genetic predispositions, not always indicating a severe medical condition
5. Myth: If you’ve had a child before, you can’t experience infertility
Fact: Secondary infertility, the inability to conceive after having one or more children, is a real issue affecting both men and women.
6. Myth: Infertility is solely a female issue if a couple can’t conceive.
Fact: Male factors contribute to nearly half of all infertility cases, highlighting the importance of evaluating both partners in a couple struggling with infertility
7. Myth: IVF (In Vitro Fertilization) is the only option for infertility treatment.
Fact: There are various fertility treatments available besides IVF, including intrauterine insemination (IUI), medication, and surgical interventions, tailored to each individual’s needs and circumstances.
8. Myth: Lifestyle choices don’t affect fertility
Fact: Lifestyle factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, poor diet, and lack of exercise can significantly impact fertility in both men and women.
Beyond the Science: Embracing Your Timeline
While this blog has explored the science behind age and fertility, remember, creating a family is a deeply personal journey. There’s no one-size-fits-all approach.
The goal is to feel empowered with knowledge and explore your options with confidence. Whether you choose to conceive naturally, explore fertility treatments, or decide to pursue adoption or a child-free life, embrace the path that feels right for you and your partner.
Summary:
Age can influence fertility, but it doesn’t have to be a barrier to parenthood. This blog explored the science behind age-related decline in egg quality (women) and sperm health (men), impacting natural conception rates.
The good news? Advancements in reproductive medicine offer options for hopeful parents at any stage. We broke down the biological factors and optimal age ranges for women (20s-30s) and the gradual decline in male fertility after 40.
Empowering you with knowledge, the blog offered actionable steps to optimize fertility at any age: a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and quality sleep. Women over 35 could explore prenatal vitamins and discuss supplements with their doctor. Men were advised to maintain a healthy weight, limit alcohol and smoking, and wear loose-fitting underwear.
For couples facing age-related challenges, the blog explored alternative paths like IVF and donor options while emphasizing personalized guidance from a healthcare professional.
Beyond science, the blog acknowledged the emotional journey. Open communication with your partner, seeking support groups or therapy, and embracing your timeline were encouraged. There’s no one-size-fits-all approach. The goal is to feel empowered to explore your options and choose the path that feels right for you and your partner.
FAQs:
- What is the optimal age range for women to get pregnant?
There’s no single “optimal” age range. However, from a purely biological perspective, women in their 20s generally have the highest chance of conception due to a higher number of healthy eggs. Fertility remains good in the 30s, but it gradually declines with age.
- How much does male fertility decline with age?
Male fertility doesn’t have a sharp decline like women’s, but sperm quality can decrease after age 40. This might involve a reduction in sperm count, motility, or morphology, potentially impacting the chances of natural conception.
- Are there any tests to assess fertility potential as we age?
Yes, various tests can assess fertility potential in both men and women. These might include blood tests to check hormone levels, semen analysis for men, and ultrasound scans for women to evaluate ovulation and the health of the uterus.
- What lifestyle changes can improve fertility for women over 35?
Prioritizing a healthy lifestyle becomes even more crucial for women over 35. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, managing stress, and getting enough sleep. Consulting your doctor about prenatal vitamins even before conception might also be beneficial.
- Can men improve sperm quality through diet and exercise?
Yes, maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and exercising regularly can contribute to sperm health. Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can also be beneficial.
- What are the success rates of fertility treatments for older couples?
Success rates for fertility treatments vary depending on factors like age, the specific treatment used, and individual health conditions. It’s important to discuss these details with a fertility specialist for personalized insights.
- Are there any risks associated with getting pregnant later in life?
While getting pregnant later in life can be safe for many women, there’s an increased risk of certain complications like gestational diabetes and high blood pressure. Regular prenatal care and close monitoring by your doctor are crucial.
- What are some emotional challenges couples might face with age-related fertility concerns?
Couples facing age-related fertility challenges might experience a range of emotions like anxiety, disappointment, frustration, and even grief. Open communication, seeking support, and potentially seeing a therapist can be helpful in navigating these emotions.
- How can couples navigate conversations about family planning and age?
Honest and open communication is key. Share your thoughts, concerns, and aspirations with your partner. Listen actively and create a safe space for both of you to express your feelings.
- What resources are available for couples facing fertility challenges due to age?
Numerous resources are available. Here are a few examples:
- The American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM): [https://www.asrm.org/](https://www.asrm.org/)
- Resolve: The National Infertility Association: [https://resolve.org/](https://resolve.org/)
- The National Institutes of Health (NIH) – Office on Women’s Health: [https://orwh.od.nih.gov/](https://orwh.od.nih.gov/)
Remember: You’re not alone. With knowledge and support, you can create a fulfilling family life, regardless of your age. Consulting a healthcare professional for personalized guidance is crucial. They can assess your individual situation, recommend appropriate fertility tests, and discuss the most suitable options for you and your partner.

