Why Am I Not Able to Conceive? What Are the Possible Reasons?
Struggling to conceive can be heartbreaking—but understanding the root causes of infertility is the first step toward finding a solution. This guide explores the most common reasons behind infertility in both men and women, and what you can do about it.

Introduction
The dream of parenthood is deeply ingrained in many of us. However, the journey to conception can often be more complex than anticipated. If you’ve been trying to conceive for several months or even years without success, you’re not alone. Infertility affects millions of couples around the world and is more common than many people realize. It can be an emotionally overwhelming experience, filled with confusion, frustration, and countless questions. But understanding infertility—its causes, signs, and treatment options—is the first step toward reclaiming hope.
Whether it stems from ovulation disorders, sperm quality issues, hormonal imbalances, or lifestyle factors, identifying the root cause is crucial. This comprehensive guide explores the most common causes of infertility in both men and women and highlights the importance of timely medical evaluation. With the right information, support, and medical care, many couples are able to overcome infertility and achieve their dream of parenthood.
Understanding Fertility
Fertility is a complex process that involves both male and female reproductive systems working in harmony. Before exploring the causes of infertility, it’s essential to understand how conception occurs and the role of various reproductive organs and hormones in the process.
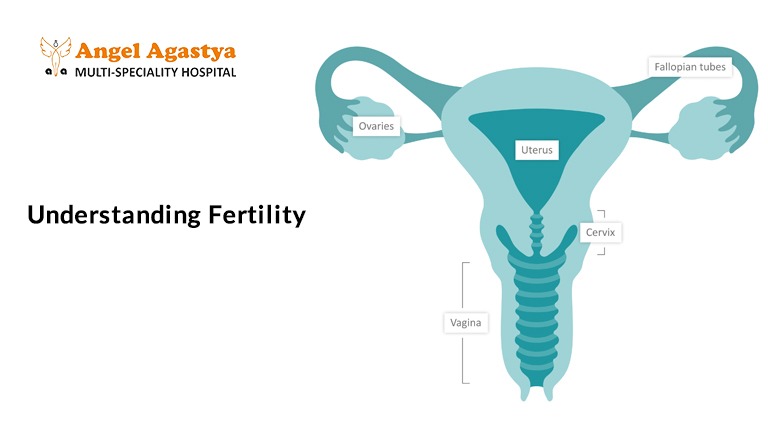
1. The Female Reproductive System
The female reproductive system consists of several key organs that work together to support conception and pregnancy:
- Ovaries – These small glands produce eggs (ova) and release one mature egg each month during ovulation. They also produce important hormones like estrogen and progesterone, which regulate the menstrual cycle.
- Fallopian Tubes – These tubes connect the ovaries to the uterus and serve as the site where fertilization occurs. The egg travels through the fallopian tube, where it may meet and be fertilized by sperm.
- Uterus – Once fertilized, the egg moves to the uterus, where it implants in the uterine lining and begins to grow into a baby. A healthy uterus is essential for a successful pregnancy.
- Cervix – This is the lower part of the uterus that opens into the vagina. It allows sperm to enter the uterus and also plays a role in protecting the uterus from infections.
For pregnancy to happen, a mature egg must be released during ovulation, travel through the fallopian tube, meet healthy sperm for fertilization, and successfully implant in the uterus. Any issues in this process can contribute to infertility.
2. The Male Reproductive System
The male reproductive system plays an equally important role in fertility by producing and delivering sperm:
- Testicles – These are responsible for producing sperm and the hormone testosterone, which is crucial for reproductive health.
- Epididymis – A coiled tube behind the testicles where sperm mature and gain the ability to swim.
- Vas Deferens – These tubes transport sperm from the epididymis to the urethra, where they mix with seminal fluid to form semen.
- Prostate Gland and Seminal Vesicles – These glands produce fluids that nourish sperm and help them survive inside the female reproductive tract.
For conception to occur, the male must produce a sufficient number of healthy sperm with strong motility (movement) so they can reach and fertilize the egg.
3. The Role of Hormones in Fertility
Hormones regulate nearly every aspect of fertility for both men and women:
- In Women: Hormones like estrogen, progesterone, luteinizing hormone (LH), and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) control ovulation and prepare the body for pregnancy. An imbalance in these hormones can disrupt ovulation and make conception difficult.
- In Men: Testosterone and FSH are crucial for sperm production and overall reproductive function. Hormonal imbalances can lead to reduced sperm count and poor sperm quality.
4. Defining Infertility
Infertility is typically diagnosed when a couple has been actively trying to conceive for:
- 12 months of regular, unprotected intercourse if the woman is under 35 years old.
- 6 months if the woman is over 35, as fertility naturally declines with age.
Infertility is a medical condition that affects both men and women, and it can often be treated with the right medical intervention. If conception is taking longer than expected, consulting a healthcare professional is an important step toward understanding and addressing potential fertility challenges.
Possible Causes of Infertility in Women
Infertility in women can be caused by a variety of factors.Understanding these potential causes can help identify the right treatment options and improve the chances of conception.
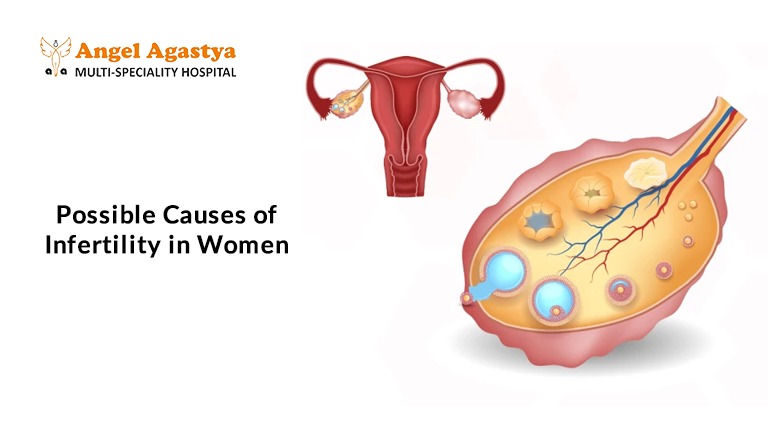
1. Ovulation Disorders
Ovulation is a key part of conception, as it involves the release of a mature egg from the ovary. When ovulation is irregular or absent, it can significantly affect fertility.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): A common hormonal disorder that leads to irregular menstrual cycles, small ovarian cysts, and elevated levels of male hormones (androgens), which can interfere with ovulation.
- Premature Ovarian Insufficiency (POI): This occurs when the ovaries stop functioning normally before the age of 40, leading to reduced egg production and early menopause-like symptoms such as hot flashes and irregular periods.
- Hypothalamic Amenorrhea: A condition in which ovulation and menstruation stop due to excessive stress, extreme weight loss, over-exercising, or a very low body fat percentage. This can disrupt the balance of reproductive hormones, making conception difficult.
2. Fallopian Tube Blockage
The fallopian tubes play a crucial role in transporting the egg from the ovaries to the uterus. If they are blocked or damaged, sperm cannot reach the egg for fertilization.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): A serious infection of the female reproductive organs, often caused by sexually transmitted infections (STIs), that can lead to scarring and blockages in the fallopian tubes.
- Endometriosis: A condition where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, potentially causing inflammation, scarring, and fallopian tube blockages. This can make it harder for the egg and sperm to meet.
3. Uterine Problems
A healthy uterus is essential for implantation and maintaining a pregnancy. Certain uterine conditions can interfere with fertility.
- Fibroids: These are noncancerous growths in the uterus that can alter its shape and interfere with implantation or pregnancy. While many fibroids are harmless, large or multiple fibroids may require treatment.
- Congenital Uterine Anomalies: Some women are born with structural abnormalities in the uterus, such as a septate uterus, which can make it difficult to carry a pregnancy to term.
4. Age-Related Infertility
As a woman ages, the number and quality of her eggs naturally decline.
- Fertility begins to decrease in the early 30s and drops more significantly after 35.
- By the time a woman reaches her 40s, the chances of conception decrease significantly, and the risk of miscarriage increases.
- Older eggs are more likely to have chromosomal abnormalities, which can affect embryo development and increase the risk of conditions like Down syndrome.
5. Other Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can disrupt reproductive hormone levels and affect fertility.
- Thyroid Disorders: Both an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) and an underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) can lead to irregular menstrual cycles and ovulation problems.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis can cause the immune system to mistakenly attack the reproductive organs, affecting fertility.
Seeking medical advice early can help identify the underlying cause and explore the best treatment options for conception.
Possible Causes of Infertility in Men
Male infertility is often related to problems with sperm production or delivery:
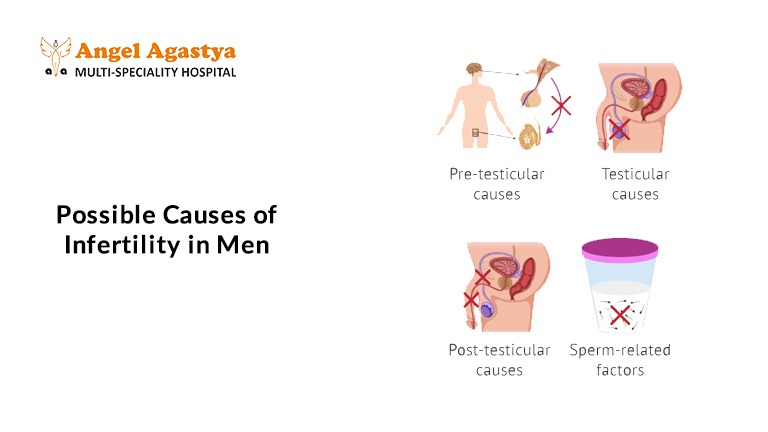
1. Sperm Disorders
- Low Sperm Count: Fewer sperm in semen reduce fertilization chances.
- Low Sperm Motility: Poor sperm movement prevents reaching the egg.
- Abnormal Sperm Morphology: Irregular sperm shape affects fertility.
2. Varicocel
An enlargement of veins in the scrotum can lead to reduced sperm quality.
3. Ejaculation Problems
- Retrograde Ejaculation: Semen enters the bladder instead of exiting the penis.
- Premature Ejaculation: Can interfere with successful conception.
4. Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal issues can affect sperm production.
5. Other Medical Conditions
- Genetic conditions (like Klinefelter syndrome).
- Infections that damage reproductive organs.
6. Lifestyle Factors
- Smoking, excessive alcohol, and drug use negatively impact sperm.
- Obesity can reduce sperm quality and hormone levels.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Infertility

1. Initial Evaluation
- Medical history review of both partners.
- Physical examination and basic fertility tests.
2. Further Testing
- Women: Hormone tests, hysterosalpingogram (HSG), laparoscopy.
- Men: Semen analysis, hormone tests, genetic testing.
3. Treatment Options
- Fertility Medications: To stimulate ovulation.
- Surgical Procedures: To correct blockages or remove fibroids.
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART): IVF, IUI (intrauterine insemination).
Lifestyle Factors and Fertility
1. Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for fertility in both men and women.
2. Nutrition & Diet
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins supports fertility.
3. Regular Exercise
Moderate exercise boosts fertility, but excessive exercise can negatively impact it.
4. Stress Management
Yoga, meditation, or therapy can help manage stress levels.
5. Avoid Smoking and Alcohol
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption harm fertility.
Conclusion
Infertility is a complex issue with a wide range of potential causes affecting both men and women. If you and your partner have been trying to conceive for a year (or 6 months if you are over 35) without success, it’s important to seek professional medical evaluation. A fertility specialist can help identify the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Remember, seeking help is a sign of strength, and many resources and support systems are available for couples facing infertility. With medical advancements and lifestyle improvements, many couples successfully overcome infertility challenges and fulfill their dream of parenthood.
FAQs
1. How long should I try before seeing a doctor?
If you’re under 35, try for one year. If you’re over 35, seek help after six months.
2. Can stress cause infertility?
Yes, chronic stress can disrupt hormone balance, affecting ovulation and sperm production.
3. Does diet affect fertility?
Yes, a nutrient-rich diet supports reproductive health, but no specific food guarantees conception.
4. Is male infertility as common as female infertility?
Yes, male factors contribute to 40-50% of infertility cases.
5. Can being overweight or underweight affect fertility?
Yes, both excess weight and being underweight can disrupt hormone levels and fertility.
6. Does age affect male fertility?
Yes, while men can father children at older ages, sperm quality declines with age.
7. Can lifestyle changes improve fertility?
Yes, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol, managing weight, and reducing stress can improve fertility.
8. Are fertility treatments successful?
Success rates depend on age and the cause of infertility. IVF success ranges from 30-50% per cycle.
9. Can hormonal imbalance cause infertility?
Yes, imbalances in estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, or thyroid hormones can impact fertility.
10. Can infertility be treated naturally?
Lifestyle changes can improve fertility, but medical intervention may be needed for specific conditions.

