How to Treat Heavy Bleeding After 40
Suddenly dealing with heavy bleeding after 40? You’re not alone, and it’s not something to ignore. This guide breaks down what’s normal, what’s not, and how to regain control with the right medical help before anxiety takes over.

Introduction
Entering your 40s can bring about many changes, and sometimes, you might experience something like heavy bleeding after 40. It’s a phase where our bodies are transitioning, and hormonal shifts can sometimes lead to unexpectedly heavy periods. While it’s natural for your cycle to change a bit during perimenopause, sudden, very heavy bleeding can be quite unsettling.
Rest assured, this kind of heavy bleeding after 40 often stems from conditions that can be managed with proper care. It’s important not to panic and instead understand the possible reasons behind it. Consulting a doctor promptly can help you get a clear diagnosis and the right treatment. We’ll explore what exactly constitutes heavy bleeding, the common causes we see, when it’s crucial to seek medical advice, and how helpful procedures like hysteroscopy can be in effectively addressing heavy bleeding after 40.
What Is Considered “Heavy Bleeding” After 40?
What do we mean by heavy bleeding after 40? It’s not just about feeling like your period is a bit heavier than usual; there are specific signs that indicate it might be more than just a typical change. As experienced gynecologists often explain, it’s about the impact this bleeding has on your daily life and your physical well-being.
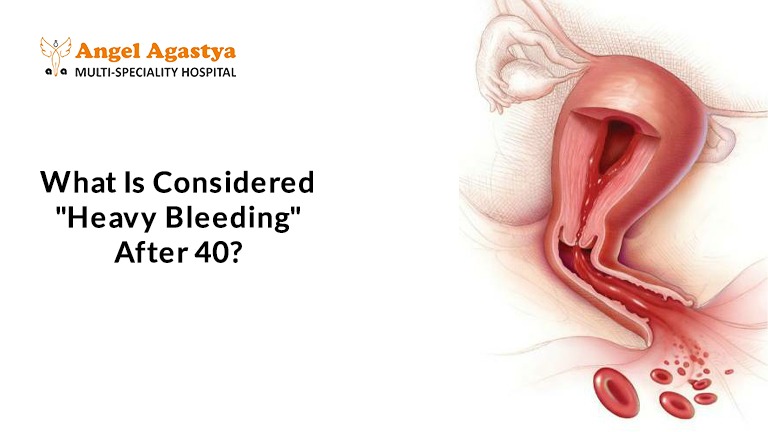
One clear sign of heavy bleeding after 40 is needing to change pads or tampons very frequently, like soaking through one or more every hour for several hours in a row. You might also find yourself having to use both pads and tampons together to manage the flow. Passing blood clots that are larger than a quarter coin is another indicator. If your period consistently lasts for more than a week, that can also be a sign.
Waking up during the night to change your sanitary protection because of heavy flow is another important clue. You might also start feeling unusually tired, weak, or even dizzy due to the amount of blood loss. Most importantly, if this heavy bleeding is significantly disrupting your daily routine, making it difficult to work, socialize, or do your usual activities due to the heavy flow or associated pain, it’s definitely something to pay attention to. It’s crucial to differentiate these signs from the normal fluctuations you might experience during perimenopause, such as periods becoming lighter or more irregular. A sudden and noticeable increase in bleeding warrants a closer look.
Common Causes of Heavy Bleeding After 40
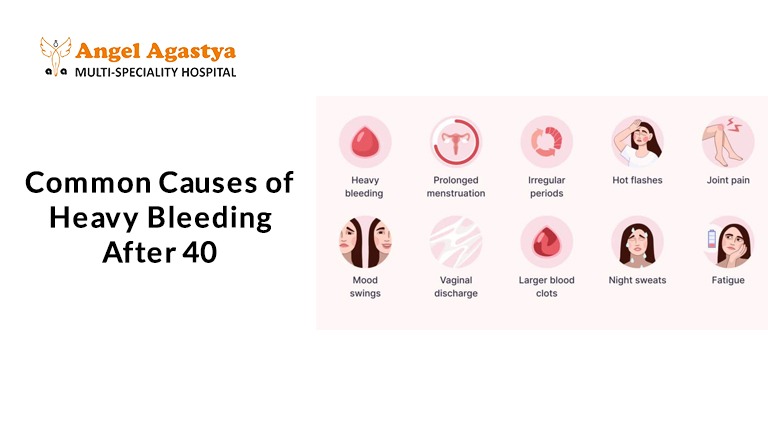
1. Hormonal Imbalances (Perimenopause)
During perimenopause, estrogen and progesterone levels fluctuate, often unpredictably. These hormonal swings can result in anovulatory cycles, where no egg is released, and the uterine lining thickens and sheds heavily later.
2. Uterine Fibroids
These are non-cancerous growths in or on the uterus. They’re common in women aged 35–50 and can cause:
- Heavy or prolonged periods
- Pelvic pressure or pain
- Bloating
3. Uterine tumors
tumors are soft, non-cancerous growths in the uterine lining. They can:
- Cause irregular bleeding
- Trigger heavy flow during periods or between cycles
4. Adenomyosis
A condition where endometrial tissue grows into the muscular walls of the uterus. It can lead to:
- Painful and heavy periods
- Chronic pelvic pain
- Enlarged uterus
5. Endometrial Hyperplasia
This is when the uterine lining becomes abnormally thick, often due to too much estrogen. It can increase the risk of endometrial cancer if left untreated.
6. IUDs (Intrauterine Devices)
- Hormonal IUDs may reduce bleeding
- Copper IUDs, however, may worsen bleeding and cramps in some women
7. Bleeding Disorders
Inherited conditions like von Willebrand disease can cause unexplained heavy periods even if they weren’t an issue earlier in life.
8. Medications
Blood thinners and certain hormonal medications can cause or worsen heavy periods.
9. Less Common But Serious Causes
In some cases, persistent heavy bleeding could be a sign of endometrial cancer or cervical cancer making prompt medical evaluation is essential.
When to See a Doctor for Heavy Bleeding After 40
- Sudden and Severe Change: Has your bleeding become dramatically heavier out of nowhere? Don’t wait, get it checked!
- Frequent Flooding: Are you soaking through pads or tampons alarmingly fast? This needs attention.
- Large Clots: Passing big blood clots frequently? It’s a sign that shouldn’t be ignored.
- Accompanying Symptoms: Are you also experiencing new pelvic pain, feeling constantly tired, or dizzy? These could be related.
- Unexpected Bleeding: Spotting or bleeding between periods or after intimacy? This warrants a visit to the doctor.
- Life Disruption: Is the heavy bleeding interfering with your daily activities and overall quality of life? It’s time to seek help.
- Persistent Issue: Has the heavy bleeding continued for multiple cycles without any improvement? Don’t delay getting it evaluated.
Remember, early detection is key to managing the cause of heavy bleeding after 40 and ensuring your well-being. Don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider for peace of mind.
Diagnostic Tests for Heavy Bleeding
Your doctor may recommend the following:
1. Pelvic Exam: To check for abnormalities in the uterus or cervix.
2. Blood Tests: To evaluate hormones, thyroid levels, and signs of anemia.
3. Transvaginal Ultrasound: A painless imaging test to examine fibroids, tumors, or a thickened uterine lining.
4. Endometrial Biopsy: Involves taking a tissue sample from the uterine lining to rule out precancerous changes.
5. Hysteroscopy: A small, lighted camera (hysteroscope) is inserted into the uterus to directly see the inside. It is one of the most precise diagnostic tools for heavy bleeding.
Hysteroscopy: A Closer Look
What is Hysteroscopy?
It’s a minimally invasive procedure that gives your doctor a clear view of your uterine cavity. It’s typically done in an outpatient setting and may cause mild cramping.
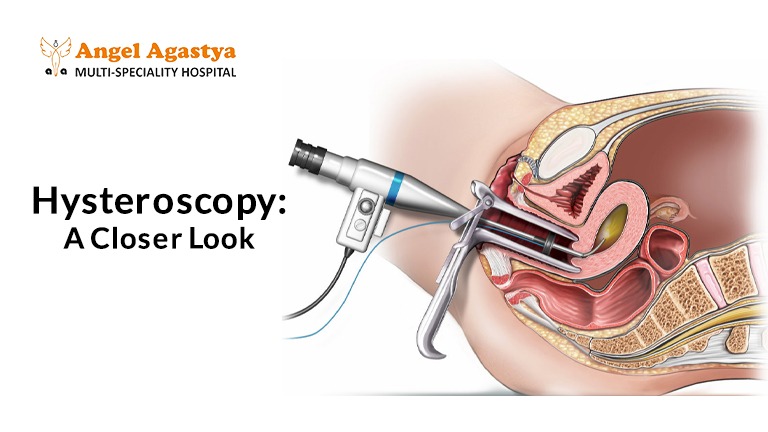
Types:
- Diagnostic Hysteroscopy: Used to observe and diagnose the cause of bleeding. It can detect fibroids, tumors, and abnormal tissues.
- Operative Hysteroscopy: Used to treat the issue immediately. Instruments can be passed through the hysteroscope to:
- Remove tumors (polypectomy)
- Remove small fibroids (myomectomy)
- Perform endometrial ablation to destroy the uterine lining and reduce bleeding
Benefits:
- No incisions
- Faster recovery
- High accuracy
- Can often treat the issue in the same sitting
Limitations:
- Not suitable for all fibroids
Endometrial ablation is not advised if you want to preserve fertility
Other Treatment Options Beyond Hysteroscopy
Your treatment plan will depend on the underlying cause and your reproductive goals. Options include:
- Hormonal Treatments: These aim to regulate your menstrual cycle and reduce heavy flow.
- Birth control pills: Can help make periods lighter and more predictable.
- Progestin-only therapy: Can be given as pills or injections to manage heavy bleeding.
- Hormonal IUDs: Release progestin directly into the uterus, often significantly reducing bleeding over time.
- GnRH agonists: Medications that temporarily shrink fibroids, which can help with heavy bleeding, though they’re not a long-term solution.
- Non-Hormonal Medications:
- Tranexamic acid: This medication helps to promote blood clotting and can be very effective in reducing the amount of blood loss during your period.
- Surgical Treatments: These are considered when medications aren’t enough or for specific conditions like fibroids.
- Myomectomy: A surgical procedure to remove fibroids while leaving the uterus intact, which is an option for women who still want to have children.
Hysterectomy: This involves the complete removal of the uterus and is usually considered as a final option when other treatments haven’t worked and the heavy bleeding after 40 significantly impacts your life.
When to Truly Worry
- Persistent Bleeding: If the heavy bleeding doesn’t subside and continues cycle after cycle, it’s a sign that needs evaluation.
- Worsening Trend: Is the heavy bleeding becoming progressively worse over time, rather than improving? This is a reason to seek medical advice.
- Accompanying Troubles: Are you experiencing other concerning symptoms along with the heavy bleeding, such as significant pelvic pain, persistent fatigue, or dizziness? These warrant attention.
While most cases of heavy bleeding after 40 aren’t caused by dangerous conditions, delaying a diagnosis can increase the risk of complications like anemia. Early evaluation often allows for less invasive treatment options and provides much-needed reassurance. Reach out to your gynecologist, early support makes all the difference.
Conclusion
Experiencing heavy bleeding after 40 is something many women go through, and you’re definitely not alone. It’s so important to remember that while it might be common, it’s not something you should just put up with quietly. Whether it turns out to be related to those trouble causing fibroids, those little tumors, the natural hormonal shifts of this time, or something else entirely, the most crucial thing you can do is pay attention to your body’s signals and reach out for medical guidance early on.
Knowing what could be causing this heavy bleeding after 40, recognizing those red flags we talked about, and understanding how helpful modern tools like hysteroscopy can be, empowers you to navigate this phase with more confidence and less worry. Please don’t let any fears or uncertainties hold you back from seeking the care and answers you deserve. Your well-being is paramount, and getting timely help can make all the difference.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Is it normal to have heavy bleeding after 40?
Some changes in your menstrual cycle are expected as you approach perimenopause, but suddenly, very heavy bleeding is not considered normal. It can be a sign of treatable issues like fibroids, tumors, or hormonal imbalance. A medical check-up is important to find the cause.
2. What are the signs that my period is “too heavy”?
You may be experiencing heavy bleeding if:
- You’re soaking through pads or tampons every 1–2 hours
- You pass large blood clots
- Your period lasts more than 7 days
- You’re feeling weak, dizzy, or tired due to blood loss
3. What causes heavy bleeding after 40?
Common causes include:
- Hormonal fluctuations during perimenopause
- Uterine fibroids or tumors
- Adenomyosis
- Thickened uterine lining (endometrial hyperplasia)
- Certain IUDs or medications
- Bleeding disorders or even, in rare cases, cancer
4. Can stress or lifestyle changes cause heavier periods?
While stress can affect your cycle’s timing, it usually doesn’t cause excessively heavy bleeding. If you notice a major change in flow, it’s best to speak to a gynecologist.
5. Should I be worried about cancer if I have heavy periods?
Heavy or irregular bleeding can occasionally be linked to endometrial or cervical cancer, especially if you are over 40. That’s why early evaluation is essential.
6. What is hysteroscopy and how does it help with heavy bleeding?
A hysteroscopy is a safe, minimally invasive procedure where a doctor uses a small camera to look inside your uterus. It can help diagnose causes like fibroids or tumors and, in some cases, treat them at the same time.
7. Will I need surgery to stop heavy bleeding?
Not always. Treatment depends on the cause and can range from medications and hormonal therapy to minimally invasive procedures like hysteroscopy. Surgery like hysterectomy is usually a last option.
8. Can heavy bleeding lead to anemia?
Yes, if left untreated, prolonged or excessive bleeding can reduce your red blood cell levels, causing iron-deficiency anemia. Symptoms include fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
9. Will my periods get lighter after menopause?
Yes. Once you reach menopause (typically around age 51) and haven’t had a period for 12 consecutive months, your periods stop. If you bleed after menopause, it must be evaluated immediately.
10. When should I see a doctor for heavy bleeding after 40?
You should consult a gynecologist if:
- Your period becomes unusually heavy
- You bleed between periods or after sex
- You pass large clots
- You feel dizzy or tired
Your bleeding affects daily activities
Early evaluation helps rule out serious conditions and guide the best treatment.

