Can Polycystic Ovary Syndrome be Treated? Can I be Pregnant if I Have PCOS?

PCOS doesn’t have to control your life or your dreams of becoming a mother. This guide reveals the 5 most effective treatments for managing PCOS, plus expert tips on how you can still get pregnant with the right approach. Don’t let myths and misconceptions hold you back—empower yourself with the truth and take action today!
Introduction
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a complex hormonal disorder affecting millions of women worldwide. It is characterized by irregular menstrual cycles, excessive androgen (male hormone) levels, and the presence of multiple small cysts on the ovaries. While PCOS can present significant challenges, it is crucial to understand that it is a manageable condition. Many women with PCOS successfully conceive and give birth to healthy babies with the right treatment and lifestyle adjustments.
Understanding Polycystic Ovary Syndrome and Fertility

PCOS is one of the most common causes of female infertility, primarily due to its impact on ovulation. Ovulation is a critical process where the ovary releases an egg, making conception possible. Women with PCOS often experience ovulatory dysfunction, making it more challenging to conceive naturally.
Irregular or Absent Periods
One of the hallmark signs of PCOS is irregular or absent menstrual cycles (amenorrhea or oligomenorrhea). The hormonal imbalances associated with PCOS disrupt the regular release of eggs, leading to unpredictable cycles or, in some cases, complete lack of ovulation.
Hormonal Imbalances and Insulin Resistance
Hormonal imbalances play a significant role in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome and fertility issues.
- Elevated Androgen Levels: High levels of male hormones (androgens) can interfere with normal ovulation and lead to symptoms such as acne, excessive hair growth (hirsutism), and male-pattern baldness.
- Insulin Resistance: A common feature of PCOS, insulin resistance means that the body’s cells do not respond efficiently to insulin, leading to higher insulin levels. This condition further disrupts hormonal balance and can contribute to weight gain and difficulty in losing weight.
- Low Progesterone Levels: Due to irregular ovulation, progesterone production is often insufficient, leading to irregular periods and potential difficulties in maintaining pregnancy.
Ovulation Problems
Women with PCOS may ovulate infrequently or not at all. Without ovulation, fertilization cannot occur, making natural conception difficult. However, several treatment strategies can help stimulate ovulation and increase the chances of pregnancy.
Treatment Options for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome

While PCOS can present challenges, it is a treatable condition. A combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and assisted reproductive technologies (ART) can help women with PCOS regulate their menstrual cycles and improve their chances of conception.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications are key in managing PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) and improving fertility, as they help address the root causes of the condition, such as hormonal imbalances, insulin resistance, and metabolic issues. Here are some ways lifestyle changes can make a significant difference:
Weight Management
Losing even a small percentage of body weight (5-10%) can significantly improve insulin sensitivity, regulate menstrual cycles, and enhance ovulation. Maintaining a healthy weight can also lower the risk of pregnancy complications, such as gestational diabetes and preeclampsia.
Healthy Diet
A PCOS-friendly diet should include:
- High-fiber foods (whole grains, vegetables, and legumes) to slow digestion and reduce insulin spikes.
- Lean proteins (chicken, fish, and plant-based sources) to promote satiety and muscle maintenance.
- Healthy fats (avocados, nuts, olive oil) to support hormone production.
- Low glycemic index (GI) carbohydrates to regulate blood sugar levels.
- Avoidance of processed foods, sugary beverages, and excessive dairy consumption, which may aggravate hormonal imbalances.
Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, jogging, strength training, and yoga, helps improve insulin sensitivity and hormonal regulation. Exercise can also help manage stress, another factor that affects ovulation.
Medications for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Treatment
Birth Control Pills
Oral contraceptives help regulate menstrual cycles, lower androgen levels, and reduce symptoms such as acne and excessive hair growth. While birth control pills do not promote ovulation, they can help manage PCOS symptoms in women not actively trying to conceive.
Metformin
Metformin, a medication commonly used to treat type 2 diabetes, is also beneficial for women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. It improves insulin sensitivity, promotes weight loss, and may help restore normal ovulation.
Fertility Medications
Women trying to conceive may benefit from medications that stimulate ovulation:
- Clomiphene Citrate (Clomid): This oral medication encourages the ovaries to release an egg, increasing the chances of conception.
- Letrozole (Femara): Originally used for breast cancer treatment, Letrozole has been found effective in inducing ovulation in women with PCOS.
- Gonadotropins: Injectable hormones that stimulate the ovaries to produce and release eggs.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
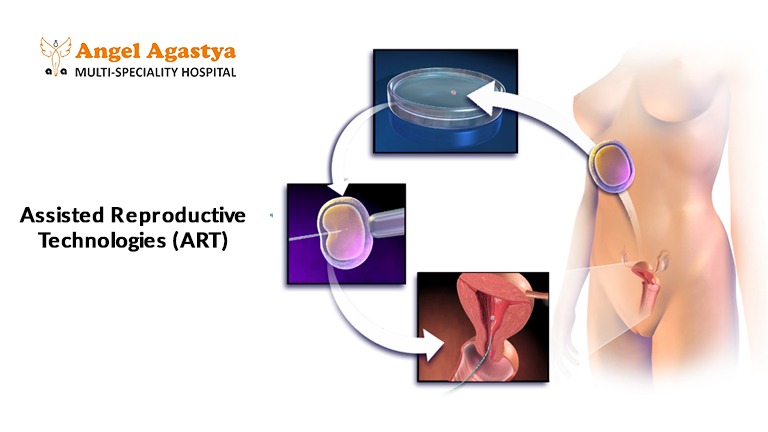
For couples who have not achieved pregnancy through lifestyle changes and medications, assisted reproductive technologies (ART) can be considered.
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
IVF is a highly effective fertility treatment for women with PCOS. The process involves retrieving eggs from the ovaries, fertilizing them with sperm in a laboratory, and then transferring the embryos into the uterus.
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)
IUI is a less invasive procedure where sperm is placed directly into the uterus around the time of ovulation to increase the chances of fertilization.
Lifestyle and Fertility
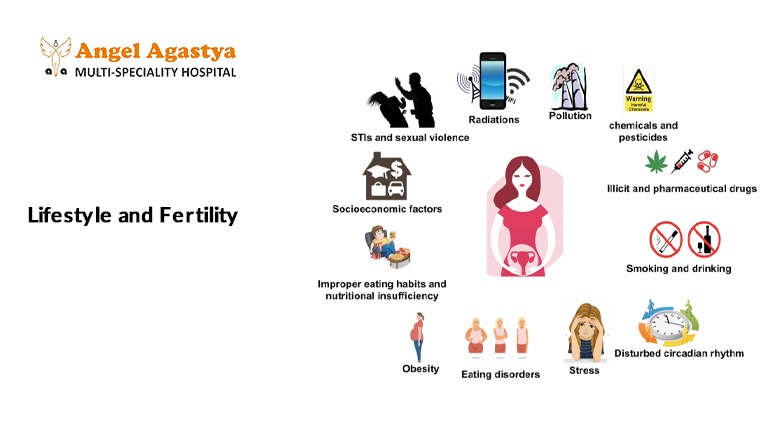
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle factors play a crucial role in improving fertility outcomes for women with PCOS.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can negatively impact hormonal balance and ovulation. Stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can improve overall well-being and enhance fertility.
Adequate Sleep
Poor sleep quality can contribute to hormonal imbalances, weight gain, and increased insulin resistance. Women with PCOS should aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
Quit Smoking and Limit Alcohol
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can significantly impact fertility. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake improves overall health and increases the chances of conception.
Can I Get Pregnant with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome?
Yes, many women with PCOS conceive naturally or with medical assistance. The key to successful pregnancy with PCOS lies in early diagnosis, effective management, and personalized treatment plans.
Factors That Influence Pregnancy Success
- Timely Treatment: Addressing PCOS-related issues early improves fertility outcomes.
- Consistent Ovulation: Achieving regular ovulation through lifestyle modifications or medication increases pregnancy chances.
- Healthy Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight optimizes hormonal balance and fertility.
- Medical Guidance: Consulting a fertility specialist can help tailor the best treatment plan for conception.
Conclusion
PCOS is a common but manageable condition that affects fertility in many women. However, with the right treatment approach—whether through lifestyle modifications, medications, or assisted reproductive technologies—women with PCOS can successfully achieve pregnancy.
If you have PCOS and are trying to conceive, working closely with your healthcare provider to develop a customized treatment plan can greatly improve your chances of a healthy pregnancy.
PCOS may present challenges, but it does not mean you cannot have a successful pregnancy and experience the joy of motherhood.
FAQs
1. What is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome?
PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) is a common hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is characterized by irregular menstrual cycles, excess androgen (male hormone) levels, and the presence of multiple cysts on the ovaries. PCOS can impact fertility, metabolism, and overall health, making early diagnosis and management essential.
2. Can Polycystic Ovary Syndrome be treated?
Yes, PCOS can be treated, but there is no permanent cure. Treatment for PCOS focuses on managing symptoms, including irregular periods, insulin resistance, weight gain, and fertility issues. Lifestyle changes, medications, and assisted reproductive technologies (ART) can help women with PCOS regulate their hormones and improve their overall health.
3. Can I get pregnant if I have Polycystic Ovary Syndrome?
Yes, women with PCOS can get pregnant, but they may face challenges due to irregular ovulation. PCOS affects fertility by disrupting the normal menstrual cycle, making it harder to conceive naturally. However, with lifestyle modifications, medications like ovulation stimulants, and assisted reproductive technologies such as IVF, many women with PCOS successfully achieve pregnancy.
4. What are the symptoms of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome?
Common symptoms of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome include:
- Irregular or missed periods
- Excess facial and body hair (hirsutism)
- Acne and oily skin
- Weight gain or difficulty losing weight
- Thinning hair or hair loss
- Dark patches of skin (acanthosis nigricans)
- Difficulty conceiving due to ovulation issues
Not all women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome experience all these symptoms, and severity varies from person to person.
5. What causes Polycystic Ovary Syndrome?
The exact cause of PCOS is unknown, but several factors contribute to its development:
- Insulin resistance: High insulin levels can lead to excess androgen production, disrupting ovulation.
- Hormonal imbalance: Increased levels of androgens (male hormones) interfere with normal reproductive functions.
- Genetics: PCOS often runs in families, suggesting a genetic component.
- Inflammation: Chronic low-grade inflammation may contribute to hormone imbalance and metabolic issues in PCOS.
6. How does PCOS affect fertility?
PCOS affects fertility by disrupting ovulation. Many women with PCOS experience anovulation (lack of egg release), making conception difficult. Additionally, hormonal imbalances and insulin resistance can further reduce the chances of pregnancy. However, with proper management, including weight control, fertility medications, and assisted reproductive treatments, many women with PCOS can conceive.
7. What lifestyle changes help manage Polycystic Ovary Syndrome?
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing PCOS:
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables can improve insulin sensitivity and hormone regulation.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity, such as walking, yoga, or strength training, helps maintain a healthy weight and reduce insulin resistance.
- Weight Management: Losing even 5-10% of body weight can improve ovulation and regulate menstrual cycles.
- Stress Reduction: Stress management techniques like meditation, deep breathing, and mindfulness can help balance hormones.
8. What are the treatment options for PCOS-related infertility?
Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome who struggle to conceive can explore several treatment options:
- Ovulation-inducing medications: Drugs like Clomiphene (Clomid) and Letrozole (Femara) can stimulate egg release.
- Insulin-sensitizing drugs: Metformin can help regulate insulin levels and improve ovulation.
- Intrauterine insemination (IUI): A fertility procedure that places sperm directly into the uterus.
- In vitro fertilization (IVF): A more advanced treatment option that fertilizes an egg outside the body before implanting it into the uterus.
9. Can Polycystic Ovary Syndrome lead to other health complications?
Yes, if left unmanaged, PCOS can lead to several health complications, including:
- Type 2 diabetes (due to insulin resistance)
- High cholesterol and heart disease
- Endometrial cancer (caused by irregular ovulation and estrogen dominance)
- Depression and anxiety (due to hormonal imbalances and body image concerns)
- Sleep apnea (more common in overweight women with PCOS)
Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent these complications.
10. Is PCOS a lifelong condition?
Yes, PCOS is a lifelong condition, but symptoms can be effectively managed through lifestyle changes, medications, and medical interventions. Women with PCOS may experience different symptoms at different life stages, such as irregular periods in their reproductive years and metabolic concerns like diabetes later in life. Long-term management strategies can help maintain hormonal balance and overall health.

