UTI (Urinary Tract Infection): A Comprehensive Guide
Struggling with discomfort and pain from Urinary Tract Infection? You’re not alone! This comprehensive guide uncovers the surprising causes, the most effective prevention strategies, and powerful treatments to help you stay healthy. Don’t let infections disrupt your life—learn how to protect your well-being today!
Introduction
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are one of the most common bacterial infections, affecting millions of people globally each year. These infections can occur in any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. While UTIs can affect both men and women, women are significantly more susceptible due to their shorter urethras, which provide a shorter pathway for bacteria to enter the urinary tract.
A UTI, though common, can become a serious medical concern if left untreated. Understanding its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies can help individuals manage and reduce the risk of developing this infection.
Understanding the Urinary Tract System

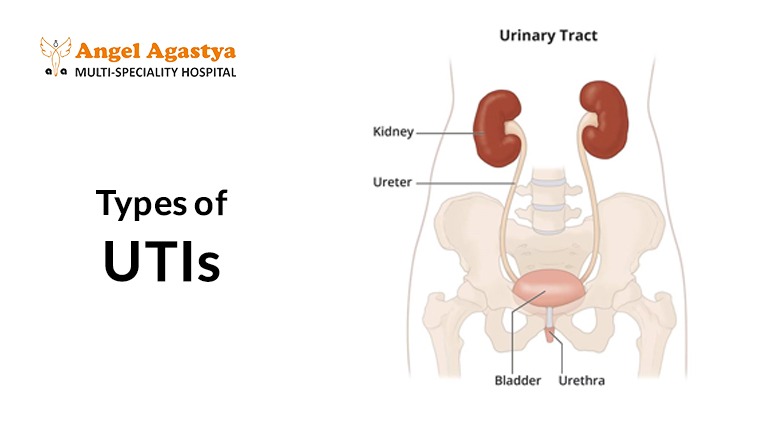
Before diving into the specifics of UTIs, it’s important to understand the urinary tract system and how it functions. The urinary system is responsible for filtering waste and excess fluids from the blood, forming urine, and expelling it from the body. It consists of:
- Kidneys – These filter waste from the blood and produce urine.
- Ureters – These are tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- Bladder – A hollow organ that stores urine until it is excreted.
- Urethra – The tube through which urine leaves the body.
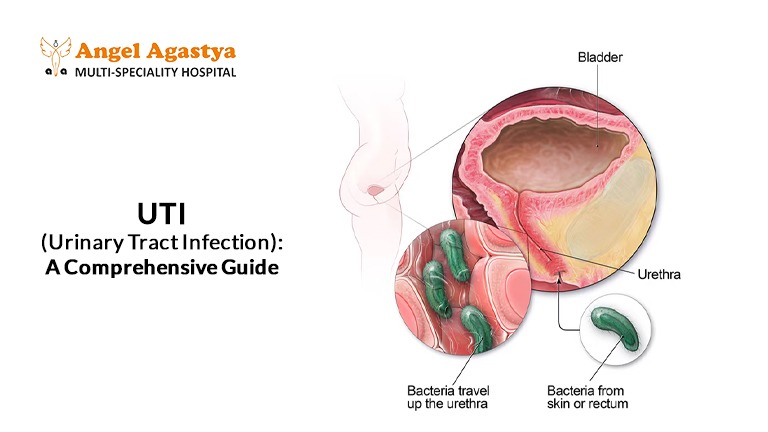
A UTI occurs when bacteria enter any part of this system, most commonly through the urethra and traveling upward.
Types of UTIs
UTIs can be categorized into two major types, depending on which part of the urinary tract is affected:
1. Lower Urinary Tract Infections
These infections affect the bladder (cystitis) and urethra (urethritis).
- Cystitis (Bladder Infection)
- The most common type of UTI.
- Symptoms include frequent urination, a burning sensation during urination, and the urge to urinate even when the bladder is empty.
- Usually caused by E. coli bacteria, which commonly reside in the intestines and can travel to the bladder.
- Urethritis (Urethra Infection)
- Affects the urethra, the tube that carries urine out of the body.
- Symptoms may include pain or discomfort during urination and, in some cases, discharge from the urethra.
2. Upper Urinary Tract Infections
These infections affect the kidneys (pyelonephritis) and are more serious.
- Pyelonephritis (Kidney Infection)
- Occurs when bacteria travel from the bladder to the kidneys.
- Symptoms include fever, chills, back pain, nausea, and vomiting.
- If left untreated, it can lead to kidney damage, bloodstream infections, and sepsis, which can be life-threatening.
Symptoms of UTI
UTI symptoms vary depending on the severity and location of the infection. The most common symptoms include:

- Frequent Urination – Feeling the need to urinate more often than usual.
- Urgent Need to Urinate – A sudden and intense urge to urinate, even if the bladder is nearly empty.
- Burning or Pain During Urination – A hallmark symptom of UTIs, described as a burning or stinging sensation.
- Cloudy or Bloody Urine – The urine may appear cloudy, discolored, or have a strong foul odor. In some cases, blood may be present in the urine.
- Pelvic Pain or Discomfort – Especially common in women, presenting as pain in the lower abdomen.
- Fever and Chills – More common in kidney infections (pyelonephritis).
- Lower Back Pain – A warning sign of infection spreading to the kidneys.
- Fatigue or Weakness – A possible indicator of a more severe UTI.
UTI Symptoms in Special Groups:
- Children – Symptoms may include irritability, poor feeding, bedwetting, or fever.
- Elderly – They may not have typical UTI symptoms but instead experience confusion, dizziness, or weakness.
Causes of UTI
UTIs are primarily caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract, the most common being Escherichia coli (E. coli) from the gastrointestinal tract. Other causes include:

- Bacterial Entry from the Anus – The urethra is close to the anus, making it easy for bacteria to travel into the urinary tract.
- Sexual Activity – Sexual intercourse can introduce bacteria into the urethra.
- Hormonal Changes – Pregnancy and menopause can alter the urinary environment, making infections more likely.
- Urinary Tract Abnormalities – Conditions such as kidney stones or an enlarged prostate can obstruct urine flow, increasing infection risk.
- Weakened Immune System – Conditions like diabetes, chemotherapy, or HIV/AIDS can reduce the body’s ability to fight infections.
- Recent Urinary Catheterization – Catheters can introduce bacteria into the bladder.
- Holding Urine for Too Long – Delaying urination allows bacteria to multiply in the bladder.
Diagnosis and Treatment of UTI
Diagnosis
UTIs are diagnosed using:
- Urinalysis – Examines a urine sample for bacteria, white blood cells, and other abnormalities.
- Urine Culture – Identifies the specific bacteria causing the infection and determines the most effective antibiotic treatment.
- Ultrasound or CT Scan – Used for recurrent or complicated UTIs to check for urinary tract abnormalities.
Treatment
1. Antibiotics
- The primary treatment for UTIs.
- Common antibiotics include nitrofurantoin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, fosfomycin, and ciprofloxacin.
- It’s crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve, to prevent antibiotic resistance.
2. Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil) can help manage pain and fever.
3. Increased Fluid Intake
- Drinking plenty of water helps flush out bacteria.
4. Rest and Recovery
- Getting enough rest and avoiding caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods can speed up recovery.
Prevention Strategies
Taking proactive measures can significantly reduce the risk of UTIs.
- Drink Plenty of Water – Helps flush out bacteria.
- Practice Proper Hygiene – Always wipe from front to back after urination or bowel movements.
- Urinate After Sexual Activity – Helps remove bacteria introduced during intercourse.
- Avoid Irritants – Harsh soaps, perfumed products, and bubble baths can irritate the urethra.
- Wear Breathable Cotton Underwear – Allows air circulation, reducing bacterial growth.
- Avoid Holding Urine for Too Long – Empty your bladder regularly.
- Consider Cranberry Products – Some studies suggest cranberry juice or supplements may help prevent UTIs.
- Probiotics and Healthy Diet – Probiotics can help maintain healthy bacteria balance in the urinary tract.
Conclusion
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are among the most common bacterial infections, affecting people of all ages and genders. While they can be painful and disruptive, they are also highly treatable with the right medical intervention and preventive measures. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is key to managing and preventing these infections effectively.
Recognizing UTI symptoms early—such as a burning sensation during urination, frequent urge to urinate, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and lower abdominal discomfort—can help in seeking timely treatment. Ignoring or delaying treatment can lead to complications, including kidney infections, which can be more severe and require intensive care. Seeking medical advice as soon as symptoms appear ensures a quicker recovery and prevents further complications.
Preventive measures play a crucial role in reducing the risk of Urinary Tract Infections. Simple yet effective steps like drinking plenty of water, maintaining proper hygiene, urinating before and after sexual activity, and avoiding irritants like harsh soaps or douches can help protect urinary health. Some studies suggest that cranberry juice or supplements may help prevent bacteria from adhering to the urinary tract lining, though they are not a guaranteed solution. It is always best to follow evidence-based medical advice and consult a healthcare provider for persistent infections.
For those experiencing frequent or recurrent UTIs, it is important to identify underlying causes. Factors such as hormonal changes, weakened immune function, anatomical abnormalities, or lifestyle habits can contribute to repeated infections. Consulting a healthcare provider can help determine the root cause and create a long-term prevention plan, which may include lifestyle adjustments, dietary changes, or prescribed medications like low-dose antibiotics.
Taking a proactive approach to urinary health is essential for overall well-being. While Urinary Tract Infections are common, they do not have to become a recurring problem. By staying informed, maintaining good hygiene, and seeking timely medical care, individuals can significantly lower their risk of infection and enjoy better urinary health. Don’t ignore the signs—prioritize your health and take the necessary steps to prevent and manage UTIs effectively!
FAQs: UTI (Urinary Tract Infection)
1. What is a UTI?
A UTI (Urinary Tract Infection) is a bacterial infection that affects any part of the urinary system, including the bladder, urethra, ureters, and kidneys. It is one of the most common infections, with symptoms like frequent urination, burning during urination, and pelvic pain.
2. What causes a UTI?
A UTI is primarily caused by bacteria, most commonly Escherichia coli (E. coli), which can enter the urinary tract from the gastrointestinal system. Other causes include poor hygiene, sexual activity, and urinary tract abnormalities.
3. What are the common symptoms of a Urinary Tract Infection?
The most common symptoms of a UTI include:
- Frequent urination
- A strong, urgent need to urinate
- Burning sensation during urination
- Cloudy or bloody urine
- Pelvic pain (in women)
- Fever and chills (in severe cases)
4. How is a Urinary Tract Infection diagnosed?
A UTI is diagnosed through:
- Urinalysis: A urine test that detects bacteria, white blood cells, and other abnormalities.
- Urine Culture: A laboratory test that identifies the specific bacteria causing the UTI and determines the best antibiotic treatment.
5. How is a Urinary Tract Infection treated?
The primary treatment for a UTI is antibiotics. Completing the full course of antibiotics is essential to prevent recurrence. Over-the-counter pain relievers, like ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage discomfort.
6. Can a Urinary Tract Infection go away on its own?
In some cases, a mild UTI may resolve on its own, but most infections require antibiotics. Delaying treatment can lead to complications, such as a kidney infection.
7. How can I prevent Urinary Tract Infection?
To reduce the risk of a Urinary Tract Infection, follow these preventive measures:
- Drink plenty of water to flush out bacteria.
- Wipe from front to back after using the toilet.
- Urinate after sexual activity to remove bacteria.
- Avoid using harsh soaps and scented hygiene products.
- Wear breathable cotton underwear.
8. Can cranberry juice prevent a UTI?
Some studies suggest that cranberry juice may help prevent Urinary Tract Infection by stopping bacteria from adhering to the urinary tract. However, it is not a guaranteed solution, and medical advice should always be sought for persistent Urinary Tract Infection cases.
9. Are women more prone to UTIs?
Yes, women are more prone to Urinary Tract Infections due to their shorter urethras, which make it easier for bacteria to enter the bladder. Hormonal changes during pregnancy and menopause can also increase the risk of Urinary Tract Infection.
10. What happens if a UTI is left untreated?
Struggling with discomfort and pain from a Urinary Tract Infection? You’re not alone! This comprehensive guide uncovers the shocking causes of Urinary Tract Infection, the most effective prevention strategies, and powerful treatments to help you stay infection-free. Don’t let a Urinary Tract Infection disrupt your life—learn how to protect your health today!
An untreated Urinary Tract Infection can spread to the kidneys, leading to a serious condition called pyelonephritis. This can cause severe symptoms like high fever, back pain, and even kidney damage or sepsis. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent complications and maintain your well-being.

