Optimize Your Nutrition & Hydration for an Painless Normal Delivery
The right balance of nutrition and hydration can make a significant difference in your labor experience. Discover essential foods, drinks, and tips to keep your body strong, energized, and prepared for a smooth, pain-free delivery.
Introduction
Pregnancy is an extraordinary journey of transformation, both physically and emotionally, leading to the possibility of a painless normal delivery. It is a time when a mother’s body becomes the sole provider of nourishment and protection for her growing baby. While the experience of pregnancy and childbirth varies from woman to woman, one universal truth remains—adequate nutrition and hydration are essential for ensuring a healthy pregnancy, preparing the body for labor, and facilitating a smooth and fulfilling birth experience.
This article explores the critical role of nutrition and hydration in supporting maternal health, promoting fetal development, and easing the process of normal delivery.
The Importance of Optimal Nutrition During Pregnancy

Pregnancy places significant demands on a woman’s body. The metabolic rate increases, nutrient needs are heightened, and the body undergoes remarkable changes to sustain both maternal health and fetal development. Therefore, a well-balanced diet is a cornerstone of prenatal care.
Supporting Fetal Development
A developing baby relies entirely on the mother for nourishment. Proper nutrition and hydration during pregnancy play a crucial role in the baby’s growth and development. Here’s how key nutrients contribute to the baby’s health.:
1. Brain Development
- Folic Acid: This nutrient is essential for forming the neural tube, which later develops into the baby’s brain and spinal cord. It helps prevent birth defects like spina bifida.
- Iron: Iron ensures the baby gets enough oxygen for brain development. It also helps prevent anemia in the mother.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: These healthy fats support the baby’s brain development and improve cognitive function and vision.
2. Bone and Tissue Growth
- Calcium: Calcium is vital for building the baby’s bones, teeth, and skeletal structure. It also supports the development of a healthy heart and nervous system.
- Vitamin D: This vitamin helps the body absorb calcium, ensuring the baby’s bones grow strong and healthy.
3. Overall Growth and Organ Function
- Protein: Known as the building block of the body, protein supports the growth of tissues, muscles, and organs in the baby. It also aids in the development of the placenta, which is essential for supplying nutrients to the baby.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Nutrients like vitamin A, vitamin C, and zinc play a key role in developing the baby’s physical features, immune system, and overall growth.
By prioritizing nutrition and hydration, mothers can ensure their baby grows healthily and reaches important developmental milestones. Focus on including nutrition and hydration through foods like leafy greens, dairy products, nuts, seeds, fish, eggs, and fresh fruits in your meals. Remember, every bite counts toward building a healthy and thriving baby, and proper nutrition and hydration are key. Nutrition and hydration don’t just benefit the baby—they keep the mother strong, energized, and ready for the journey of childbirth. Staying mindful of nutrition and hydration ensures both mother and baby remain healthy throughout pregnancy and delivery.
Enhancing Maternal Health

Good nutrition during pregnancy not only supports the baby but also helps the mother stay healthy, strong, and ready for the challenges of pregnancy, labor, and recovery. A well-balanced diet has multiple benefits for maternal health:
1. Boosting Energy and Stamina
Pregnancy demands extra energy, as the mother’s body is working to support the baby’s growth. Eating nutrient-rich foods provides the calories and essential nutrients needed to fuel the body. This energy is especially important during labor, which requires significant physical strength and stamina. A balanced diet helps prevent feelings of fatigue and keeps the mother active throughout her pregnancy.
2. Reducing Risks of Pregnancy Complications
Deficiencies in essential nutrients can lead to complications such as anemia, preeclampsia, and gestational diabetes. For example:
- Iron: Prevents anemia, ensuring the mother has enough red blood cells to supply oxygen to the baby.
- Calcium: Reduces the risk of high blood pressure and preeclampsia while supporting the mother’s bone health.
- Fiber and Whole Grains: Help prevent constipation and regulate blood sugar levels, lowering the risk of gestational diabetes.
By eating a variety of healthy foods, mothers can lower the chances of these complications and maintain better overall health.
3. Supporting Emotional Well-Being
Pregnancy often brings emotional ups and downs, but certain nutrients can help stabilize mood and reduce stress:
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds, these healthy fats support brain health and help reduce anxiety and depression.
- B Vitamins: Found in whole grains, eggs, and leafy greens, these vitamins play a key role in supporting the nervous system and improving energy and mood.
Key Tips for Maternal Health
To stay healthy, mothers should prioritize nutrition and hydration by eating a variety of foods, including fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, dairy products, and healthy fats. Proper nutrition and hydration are essential for maintaining energy levels and overall well-being. Eating small, frequent meals can help manage nausea and ensure steady energy. Additionally, staying hydrated is crucial, as nutrition and hydration support digestion and prevent dehydration, making them key factors for a healthy pregnancy and smooth delivery.
By focusing on proper nutrition, pregnant women can ensure their own health and well-being while creating the best possible environment for their growing baby. A strong, healthy mother is better equipped for labor, delivery, and caring for her newborn.
Key Nutrients for a Healthy Pregnancy

1. Folic Acid
Folic acid is indispensable during early pregnancy, reducing the risk of neural tube defects such as spina bifida. Pregnant women are advised to consume at least 400-600 mcg daily.
Sources: Leafy greens (spinach, kale), citrus fruits, avocados, beans, and fortified cereals.
2. Iron
Iron supports the production of hemoglobin, which is essential for carrying oxygen to the baby and preventing maternal anemia. Pregnant women require nearly double the iron intake compared to non-pregnant women.
Sources: Lean meats, fish, eggs, lentils, tofu, and fortified grains.
3. Calcium
Calcium is critical for developing the baby’s bones, teeth, heart, and nervous system. It also helps prevent maternal bone density loss.
Sources: Dairy products, fortified plant milk, almonds, broccoli, and sesame seeds.
4. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
These fatty acids are essential for the baby’s brain development, improving cognitive function and vision.
Sources: Fatty fish (salmon, sardines), chia seeds, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
5. Protein
Protein is often referred to as the building block of life. It is necessary for developing fetal tissues, muscles, and organs.
Sources: Chicken, eggs, dairy, lentils, quinoa, and soy products.
Hydration: The Cornerstone of a Healthy Pregnancy

While nutrition and hydration are paramount, nutrition and hydration are equally critical in supporting maternal and fetal health. Nutrition and hydration play a vital role in nearly every physiological function in the body, and the importance of nutrition and hydration grows significantly during pregnancy.
The Role of Water During Pregnancy
- Transporting Nutrients and Waste
- Water aids in delivering essential nutrients to the fetus and removing waste products through the placenta.
- Maintaining Amniotic Fluid Levels
- Amniotic fluid cushions and protects the baby, and its volume depends on the mother’s hydration levels.
- Preventing Dehydration
- Dehydration during pregnancy can cause fatigue, headaches, dizziness, and even premature contractions.
- Regulating Body Temperature
- Water helps the body maintain a stable temperature, especially during the physical exertion of pregnancy and labor.
Tips for Staying Hydrated
- Aim for at least 8-12 glasses of water daily.
- Carry a reusable water bottle to encourage frequent sipping.
- Include hydrating foods like watermelon, cucumbers, oranges, and lettuce in your diet.
- Limit caffeinated beverages, as they can increase fluid loss.
Dietary Guidelines for a Healthy Pregnancy
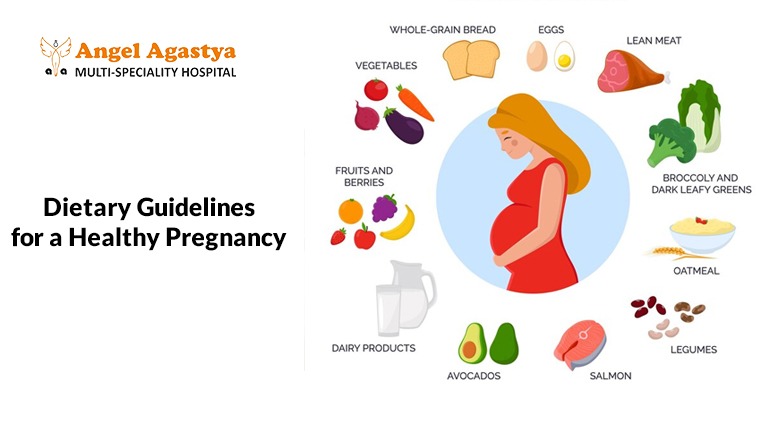
Maintaining a balanced diet involves a combination of mindful choices, portion control, and addressing individual nutritional needs.
Focus on Whole Foods
Prioritize unprocessed, nutrient-dense foods over refined or sugary options. Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats should form the foundation of your diet.
Practice Mindful Eating
- Avoid overeating by tuning into your body’s hunger and fullness cues.
- Eat meals slowly, savoring each bite to improve digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Minimize distractions like TV or phone use during meals.
Listen to Your Body
Pregnancy cravings and aversions are normal. While it’s okay to indulge occasionally, focusing on nutrition and hydration can help you make healthier choices. Prioritizing nutrition and hydration ensures that your body gets essential nutrients while satisfying cravings in a balanced way. Whenever possible, opt for healthier alternatives that support your overall nutrition and hydration during pregnancy. If you suspect a food intolerance or allergy, consult your healthcare provider.
The Role of Nutrition in Labor and Delivery
Proper nutrition during pregnancy not only promotes fetal growth but also prepares the mother’s body for the demands of labor and delivery.

1. Energy Levels
Labor requires tremendous physical effort, akin to running a marathon. Consuming complex carbohydrates, healthy fats, and protein in the weeks leading up to delivery ensures the mother has adequate energy reserves.
2. Muscle Strength and Endurance
Protein-rich foods contribute to strong, resilient muscles, which are essential during labor contractions and delivery.
3. Managing Complications
Nutritional deficiencies can exacerbate complications such as fatigue, prolonged labor, or difficulty healing postpartum. Maintaining a balanced diet helps mitigate these risks.
Foods to Include in a Labor-Prep Diet

- Complex Carbohydrates
- Whole grains, sweet potatoes, and oats provide sustained energy during labor.
- Healthy Fats
- Avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil support hormone production and energy storage.
- Hydration-Boosting Foods
- Water-rich fruits like watermelon and oranges help maintain hydration during labor.
- Iron-Rich Foods
- Ensure optimal oxygen transport by consuming iron-rich options like spinach and lentils.
- Electrolyte-Rich Snacks
- Coconut water, bananas, and yogurt help balance electrolytes, reducing fatigue during labor.
Conclusion
Nutrition and hydration are the foundations of a healthy pregnancy and a painless, smooth delivery. By consuming a nutrient-rich diet, staying hydrated, and listening to your body’s needs, you prepare not only for the arrival of your baby but also for a positive labor experience. Proper nourishment enhances maternal health, supports fetal development, and equips your body to face labor’s physical demands with strength and resilience.
Every bite and sip you take during pregnancy is an act of love and care for yourself and your growing baby. By prioritizing wholesome foods and maintaining adequate hydration, you set the stage for a joyous and empowered birth experience—one where you are nourished, strong, and ready to welcome your child into the world.
FAQs on Nutrition and Hydration for a Painless Normal Delivery
Why is proper nutrition important for a painless normal delivery?
Proper nutrition provides the energy, strength, and resilience needed during labor. It supports fetal development and ensures the mother’s body is well-prepared for the physical demands of delivery.
What are the essential nutrients for a healthy pregnancy?
Key nutrients include folic acid (for neural tube development), iron (for oxygen transport), calcium (for strong bones), omega-3 fatty acids (for brain development), and protein (for tissue and organ growth).
How does hydration help during pregnancy and labor?
Hydration aids in nutrient transport, maintains amniotic fluid levels, prevents dehydration, and regulates body temperature. It also helps the body function efficiently during labor and delivery.
What foods should I prioritize for a balanced pregnancy diet?
Focus on whole foods such as leafy greens, whole grains, lean proteins, nuts, seeds, fruits, and healthy fats like avocado and olive oil.
What are some tips for staying hydrated during pregnancy?
Drink 8–12 glasses of water daily, carry a reusable water bottle, include water-rich foods like watermelon and cucumbers in your diet, and limit caffeine intake.
Can proper nutrition and hydration reduce labor pain?
Yes, a well-nourished and hydrated body is better equipped to handle labor’s physical demands. This can lead to improved energy levels, stronger muscles, and a smoother delivery process.
How does protein help during labor and delivery?
Protein strengthens muscles, supports tissue growth, and improves muscle endurance, all of which are essential for managing contractions and pushing during delivery.
What are the risks of poor nutrition during pregnancy?
Poor nutrition can lead to complications like anemia, preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, fatigue, and prolonged labor. It can also affect the baby’s growth and development.
What foods should I eat in the weeks leading up to delivery?
Include complex carbohydrates (e.g., oats, whole grains), healthy fats (e.g., nuts, avocados), iron-rich foods (e.g., spinach, lentils), and hydration-boosting options like coconut water and water-rich fruits.
How can I manage pregnancy cravings and ensure balanced nutrition?
While occasional indulgence is fine, try satisfying cravings with healthier alternatives. Listen to your body, and if you suspect a nutrient deficiency, consult your healthcare provider for guidance.

